Introduction
ROP Emporium训练6:pivot的解析。
pivot32
Step 1
程序正常运行截图:
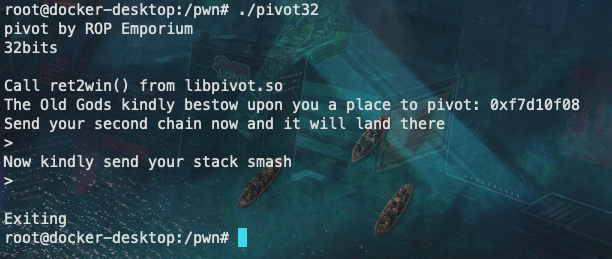
发现可能存在内存地址泄露,加上题目给了libc.so文件,猜测可能需要用到ret2libc和延迟绑定技术,详细内容可了解ret2libc && Lazy Binding。
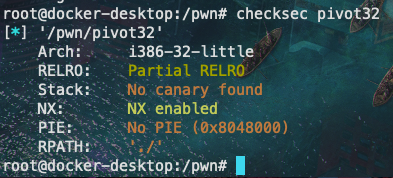
checksec:
Step 2
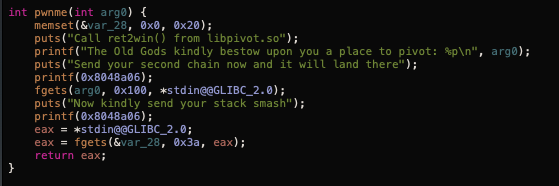
pwnme函数中fgets函数存在溢出漏洞,offset为0x28:
程序运行时提示我们call ret2win() from libpivot.so,看下这个函数是什么内容:
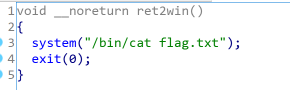
那么直接调用这个函数就行了。但是这个函数在libc.so中,需要通过ret2libc实现函数的调用。首先要选择一个函数同时在pivot程序和libc.so中,泄露其真实地址后通过计算得到libc.so加载的基址,加上ret2win函数在libc.so中的offset,直接定位ret2win函数在内存中的真实地址。
通过比对发现,我们只能选择foothold_function函数来获取libc.so的基址:
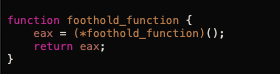
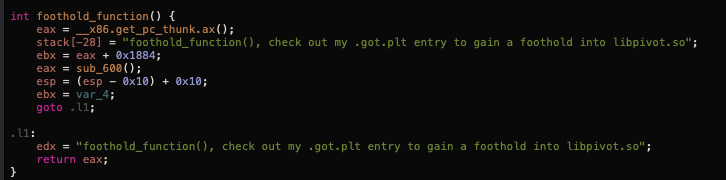
这时我们会发现pwnme函数中fgets只有0x3a Bytes缓冲区的长度,并不足以存放我们的shellcode,所以需要另找一个位置存放shellcode。
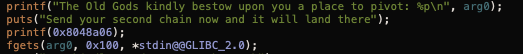
好在程序给了我们一块0x100的堆空间,且具体的内存地址也告诉我们,但是我们需要考虑如何把shellcode写到给的地址上去。

通过上面的几个函数就可以实现将shellcode写到指定的内存地址。
到此,思路就比较清楚了:第一步先将shellcode写到指定内存地址,第二步利用溢出漏洞使程序跳转到shellcode执行。
第一步中通过sub_80488c4函数写入,通过sub_80488c0函数控制eax寄存器。为了将栈转移到我们需要的地址,需要通过sub_80488c2控制esp寄存器。在找到libc.so的加载基址后,需要通过sub_80488c7函数将基址加上offset找到ret2win函数在内存中的真实地址。所以我们还需要找到控制ebx寄存器的指令:
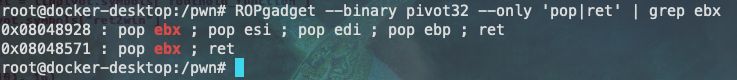
第二步中我们还需要一条指令在覆盖fgets函数返回地址后使得程序能够跳转到我们设定的内存地址执行shellcode,由于我们通过sub_80488c4函数将地址写到了eax寄存器中,所以我们需要控制程序跳转的eax寄存器指向的地址:

这样一切准备工作就完成了。
Step 3
下面就是EXP的编写:
1 | * # coding:utf-8 |
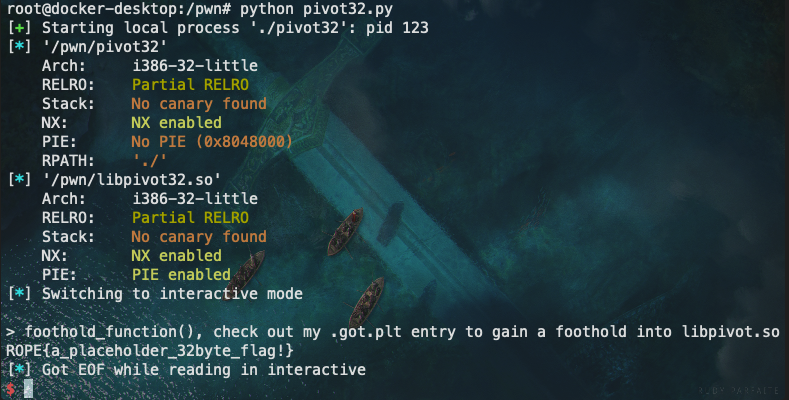
- 脚本运行结果图:
pivot
64位程序和32位思路一模一样,EXP也基本相同,有兴趣的可以自行尝试。